Virtual & Cloud-Based Installation
Local/Server
Installing OPNsense on a virtual machine can be done by using the DVD ISO image. Full instructions are available in chapter Initial Installation & Configuration.
General tips
For optimal performance and compatibility, consider the following guidelines:
Minimum required RAM is 3 GB
Minimum recommended virtual disk size of 8 GB
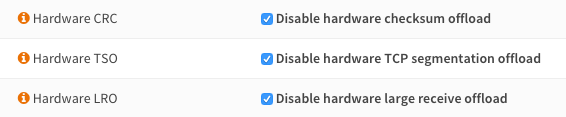
Disable all hardware off-loading settings in
VMware ESXi
VMware offers full instructions for installing FreeBSD, which can be found here.
To install VMware Tools, go to and install os-vmware by clicking on the + sign next to it.

Note
While other network setups may work fine, it is recommended to use VMXNET3 according to VMware’s Compatibility Guide.
Xen
To install Xen tools, go to (tick Show (Tier 3) community plugins) and install os-xen by clicking on the + sign next to it.

Hyper-V
Both Hyper-V Generation 1 and 2 virtual machines are supported out of the box with no additional drivers or tools needed.
Note
Secure Boot must be disabled in the Hardware > Security section of the VM.
KVM
To install QEMU Guest Agent, go to (tick Show (Tier 3) community plugins) and install os-qemu-guest-agent by clicking on the + sign next to it.
KVM chipsets OPNsense (based on FreeBSD) supports running under both the legacy i440FX machine type and the newer Q35 chipset.
Others
OPNsense can be installed on all hypervisors that support FreeBSD (such as Bhyve or VirtualBox).
Note: to install VirtualBox Guest Additions, go to (tick Show (Tier 3) community plugins) and install os-virtualbox by clicking on the + sign next to it.
Hosted
For hosted installations where you cannot install using the DVD ISO, an alternative approach is available in the form of opnsense-bootstrap.
opnsense-bootstrap
opnsense-bootstrap(8) is a tool that can completely reinstall a running system in place for a thorough factory reset or to restore consistency of all the OPNsense files. It can also wipe the configuration directory, but won’t do that by default.
It will automatically pick up the latest available version and build a chain of trust by using current package fingerprints -> CA root certificates -> HTTPS -> OPNsense package fingerprints.
What it will also do is turn a supported stock FreeBSD release into an OPNsense installation. Both UFS and ZFS installations are supported.
opnsense-bootstrap is available at our GitHub source repository
Amazon AWS EC2 Cloud

Installing OPNsense in Amazon Web Services can be a daunting task as no console is offered. Luckily, an easy-to-install AMI is available in the AWS Marketplace.
See our how-to for Installing OPNsense AWS image.
Microsoft Azure

OPNsense is available in the Microsoft Azure Marketplace as an easily installable virtual appliance.
See our how-to for OPNsense Azure Virtual Appliance.
Common Issues
Some common issues have been reported for different virtual environments. You can find known solutions to these problems below.
If your problem is not listed, always try the General tips mentioned in this article first.
File copy failed during installation
This issue is most likely caused by a low memory setting. Make sure your virtual OPNsense installation has a minimum of 3 GB of RAM.
Disk Errors on VMware
This issue can be caused by a defective drive. Changing the drive mode to IDE has been reported to help for certain ESXi versions.
NAT / performance issues on XenServer/XCP-NG
This issue has been reported to be solved by disabling TX checksum offloading on Vifs (only there, not also in OPNsense DomU) - for details see this documentation.
Traffic Shaper does not work on VMware
If you are using the VMXNET3 driver, try switching to E1000 instead.